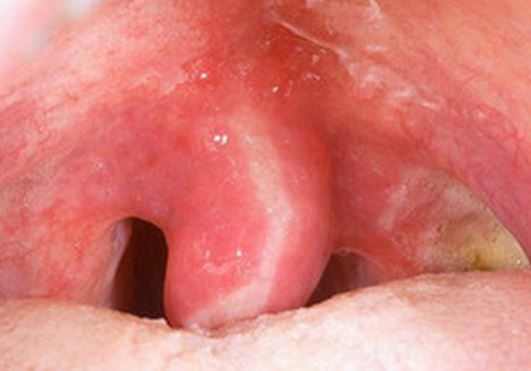
A swollen uvula can be caused by an infection, STD, glandular fever, or even after surgery, such as tonsillectomy. A sore throat, strep, and sometimes no pain, but white spots are reported as symptoms associated with its enlargement.
When the inflammation is severe, the uvula can touch the tongue and irritate the back of the throat.
Here’s more on the causes and treatment to get rid of the inflamed uvula, as well as what you can do at home to relieve your symptoms.
The uvula is also called the palatine uvula. It is the fleshy structure that hangs in your throat. Most people confuse it with tonsils. The work of the palatine uvula is to filter bacteria and prevent them from entering the digestive system as well as the respiratory system. So, how does it feel to have a uvula that is swollen, and what does it mean?
Enlarged or elongated uvula (meaning)
A swollen uvula means that the structure is inflamed, irritated and sometimes, enlarged. The reason behind this could be an infection, irritation from alcohol, smoking, or some spices. We have discussed the causes of an inflamed uvula and what it means when some symptoms show up below.
The medical term used to refer to an enlarged and inflamed palatal uvula extension is uvulitis. In a general sense, according to Drugs.com, uvulitis refers to severe swelling. This, as reported by the Scott and White Memorial Hospital, may show signs such as soreness and redness, all of which are signs of inflammation.
Can uvulitis kill you, or is it life-threatening?
Uvulitis is not a life-threatening condition and is not likely to kill you. The inflammation should go away on its own after a few days.
Sometimes, treatment may be required to get rid of the bacteria, viruses, and yeast cells that may make it remain persistent.
How long will a swollen uvula last?
For people who wake up with the swelling at the back of the throat, the inflammation can last just a few hours if the primary cause is snoring. However, the symptom can last from a few hours to a few days, and in severe cases, it can take weeks to heal.
Treating the cause is the best way to stop the swelling fast. Leaving it to heal on its own means you might experience the swelling for a little longer, maybe days or even weeks.
Causes of inflammation
Why is my uvula swollen after tonsillectomy, drinking, or when I am dehydrated? These are the few most common causes of uvulitis.
In people who snore, shout a lot, or involve themselves in sports, a sore uvula is a common occurrence. Nonetheless, below are the reasons why you get uvulitis in your throat.
1. Tonsillectomy or swelling after surgery
Sinus surgery, tonsillectomy surgery, and intubation or laparoscopic surgeries around the nose and throat may all cause a swollen or inflamed uvula.
Dr. David J. Kiener, MD on Realself, says that it is not unusual for a patient to have a sore uvula after surgery, from anesthesia.
The swollen uvula after surgery is usually a result of “irritation by the endotracheal tube used to maintain the airway.” Bacterial infections may worsen the symptoms. Otherwise, the swelling should resolve on its own within 10 days. Other operations that may cause an inflamed uvula include wisdom teeth removal that involves anesthesia injection.
2. Drinking alcohol
People who suffer from a swollen mouth, throat, and uvula from drinking alcohol may be suffering from alcohol allergy.
Another explanation is that your throat and other organs in the mouth may swell due to dehydration.
Alcohol causes dehydration, and the following morning, the hangover headaches may be accompanied by swollen tonsils, swollen sore throat, swollen taste buds on your tongue, and uvulitis.
3. Dehydration
Can dehydration cause the uvula to swell or enlarge? When your body does not have enough water in it, a dry throat is experienced. This is common in people who drink alcohol or smoke regularly.
In case an inflamed uvula is caused by dehydration, drink at least 8 glasses of water. Other beverages and fluids such as orange juice may help hydrate your body and relieve the swelling in your throat.
4. Allergies and hay fever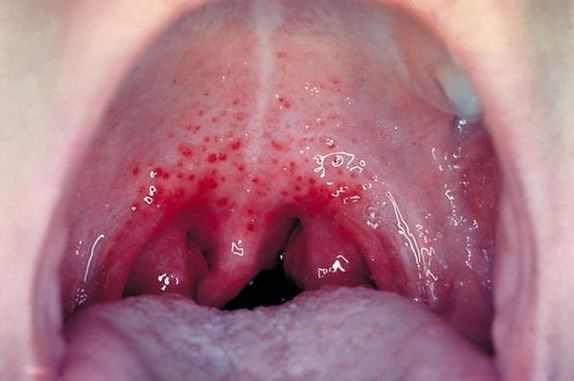
Abrupt swelling of the uvula, tissues in your mouth, and back of the throat is usually a sign of allergic reaction. This is also called edema. Such a response is called an anaphylactic reaction that is dangerous and should be considered an emergency.
Allergic reactions in the throat are sometimes treated with a shot of epinephrine. However, you should identify the foods you are allergic to and avoid them to prevent a swollen uvula and mouth.
5. STDs, oral thrush, yeast
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as HIV and herpes (HPV) are also responsible for an array of symptoms in the throat, such as bumps in the throat and tongue, yellow tongue, and even bleeding and swollen tissues in the mouth.
Irritations from viral infections and even yeast infections such as oral thrush can cause your uvula to be swollen and sore.
While, in most cases, it is less likely to be an STD problem, people who have oral sex may be prone to such throat inflammations.
6. Throat bacterial infections
Most infections in the throat may cause tissues in the oral cavity to swell. This includes the uvula. Both bacterial and viral infections, including strep throat, epiglottitis, and mononucleosis (mono), are responsible for such inflammation.
Epiglottitis is common in young children where the epiglottis tissue – attached to the end of the tongue – swells. It can result in breathing problems. Infections in the throat should be treated as soon as possible to reduce their risks.
7. Singing or yelling, injury and stress
Physical trauma and injury to the uvula are a source of physical stress that can cause it to swell. You are likely to experience a swollen uvula from yelling or singing too much. Other sources of trauma and stress include:
- Burned uvula from hot foods or drinking hot beverages.
- Intubation or Insertion of a breathing tube in the throat can also cause trauma to the uvula.
These cause minor swelling that goes away when treated by drinking cold fluids and avoiding spicy foods such as hot pepper.
8. Strep throat
Streptococcal bacteria in the throat cause an infection that leads to symptoms such as pain in the throat, swelling of membranes and mucous tissues in the mouth, tonsils, and back of the throat.
When you have strep throat, you will experience a sore throat as well. The uvula, as part of the throat, becomes swollen as a result of strep throat infections.
9. Smoking

People who smoke and those who work in areas that are highly polluted are reported to have more cases of swelling of the throat and uvula.
According to The Student Room, smoking acts as an irritant or pollutant in the oral cavity. It causes the mouth to dry up.
When the uvula and back of the throat dry up, you become itchy and irritated. This may cause swelling and irritation of tonsils, epiglottis, tongue, and uvula. Vaping, smoking weed, and even e-cigarettes can all cause the swelling.
10. Acid reflux and vomiting
The uvula may swell due to GERD (acid reflux) and vomiting (throwing up or puking). These two can irritate the throat because of the acid that is being regurgitated into the throat area and even in the mouth. You might find bumps at the back of the tongue.
Acid reflux and nausea are common during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester. It can be treated with over the counter and prescription medications, though since it is not a life-threatening condition.
11. Breathing through the mouth while sleeping
Did you know that breathing through your mouth dries up the throat? If you wake up every morning with an inflamed uvula, you could be breathing through the mouth at night.
Apart from sleeping with mouth open, snoring, and sleep apnea, as we shall see below, are majorly to blame for an irritated and enlarged uvula in the morning.
12. Other reasons for an irritated uvula
A painful, enlarged or elongated uvula can also be caused by other factors listed below.
- Cancer and growths in the throat
- Cold
- Some drugs and medications may irritate the throat. Zlosoft side effects may include swelling of the face and mouth.
- Glandular fever
- Lupus disease
- Laryngitis, where there is swelling of tissues from the level of the epiglottis towards the voice box or larynx.
- Sleep apnea disorder
- Hereditary angioedema
- Postnasal drip side effects
You can relieve a swelling uvula with home remedies. Still, you must see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment because some of these causes can be difficult to cure at home, naturally. So what additional signs should you look for before determining what to do?
Symptoms of uvulitis
Uvulitis is usually a symptom of another infection or disease. It is likely to go away on its own, but when it is recurring, you should see a doctor. The following are the symptoms of uvulitis to look out for.
- A painful uvula and ear: Patients may complain of pain in the throat, on the uvula, and even in the ear. The infections can quickly spread to the ear and cause discomfort. When the uvula hurts, the pain is a result of inflammation from bacteria and viruses.
- Enlarged, hanging, or elongated uvula: The primary symptom of uvulitis is an enlarged uvula. It increases in size, usually described as elongated and hanging. The uvula can swell and touch the tongue, causing gag reflex and nausea that won’t go away.
- Uvula causing gagging or constant nausea: A long uvula that touches the back of the tongue can cause discomfort due to gagging and feeling of nausea. It is similar to inserting your finger down your throat.
- Cough and nasal congestion: A long and floppy uvula causes mechanical irritation, according to the Postgraduate Medical Journal. Nasal congestion may also be experienced due to the irritation of the upper airways in your respiratory system.
- White stuff or pus in your throat: Pus or white things/stuff on tonsils and uvula point to an infection. If you see white spots, patches, or coating on the uvula and a yellow coating on the tongue, it could be a sign of a viral or bacterial infection in your throat.
- Red spots or inflammation: A reddened structure in the throat, unusually colored, is a sign of swelling up of the uvula.
- Losing voice or hoarse voice: Your voice is produced clearly when there is the unobstructed passage of air from your larynx to the oral cavity. When the uvula swells, it interferes with the quality of your voice. You will either lose your voice, or it will be worse when the uvula swells.
- Chocking or difficulty in swallowing: Uvulitis can obstruct the throat and interfere with normal swallowing of food. This will be worsened when the structure is painful. When it hurts or is hard to swallow food, it could be a result of an inflamed and enlarged uvula.
Other symptoms of an extremely swollen uvula include swollen lymph nodes due to inflammation and sometimes small lumps in the throat.
Swollen uvula from snoring
Snoring is often mentioned as a cause of an enlarged uvula. According to MedicineNet, after a night of heavy snoring, the uvula and soft palate may be swollen in the morning. The cause of this is that snoring flaps around the uvula, blocking the airway and causing breathing problems.
You might complain of a mild sore throat, sleep apnea, and other sleep disorders. Snoring in itself is also known to cause a swollen throat and organs around it because of the heavy breathing and the flapping around of the hanging extension in the back of the throat.
When the uvula causes snoring, excision may be the option to help you stop snoring permanently. However, Dr. Christopher Chang of Faquier ENT notes that uvula removal is not a conclusive treatment for obstructive sleep apnea.
Sore throat, no pain, no tonsils
Sore throat is one of the most common symptoms of an irritated uvula. A sore throat may come with no other symptoms, but in most cases, an itchy throat, pain and irritation, and sometimes cough accompany this problem.
When you have a sore throat and an enlarged uvula, you could be suffering from a bacterial infection. But what does it mean to have a swollen uvula, no pain, and no tonsils? Most likely, physical trauma and some viral infections may show no other symptoms. If the swelling persists for more than 2 days, see a doctor for treatment.
When it is not going away for a week
What is the recovery time of a uvula swelling? How long the swelling will last depends on the cause. If you have just had a tonsillectomy, you should expect to recover within 7 to 10 days, according to HealthGuide HQ.
However, you might have uvulitis not going away for a week or even months, or keeps recurring. In such a case, you could be having recurring infections in the throat that cause it. For uvulitis that won’t go away, see a doctor for treatment and advice.
Relief for an enlarged uvula
To get rid of uvulitis, home remedies, cures, and medical treatments can help. It is also essential to know when to see a doctor as an emergency case.
Antibiotics are prescribed for the treatment of bacterial infections such as strep throat. Anti-fungal medications may be administered to help get rid of swelling caused by yeast and oral thrush. Here’s how to get rid of a swollen uvula fast.
Treatment and medications
Medications and over the counter treatments can be used to fix a swollen throat. Here are the medicines that are used to treat an inflamed uvula.
- Antibiotics: Anti-microbial medications and antibiotics treat the cause when it is a bacterial infection. Broad-spectrum antibiotics will be administered by your ENT doctor to help kill the microorganisms irritating your throat. To shrink a swollen uvula completely, follow your full course of antibiotics.
- Antihistamines or anti-inflammatory medicine: Antihistamines are anti-inflammatory medications that will shrink swollen glands and uvula if caused by allergies. Examples of medications usually given are Benadryl and Zyrtec.
- Steroids: Your doctor might also recommend steroids to get rid of food allergies and also help relieve pain.
- Pain killers to relieve the pain: For people experiencing pain when swallowing or breathing, painkillers such as ibuprofen can help reduce the pain.
- Surgical removal of the uvula: Surgery is only done in extreme cases where the swelling is life-threatening.
Home remedies
Home remedies for inflamed uvula include water gargles, cold treatment to relieve the swelling, natural antibacterial, and antivirals such as honey and herbs like turmeric. Below are ways to get rid of an inflamed uvula naturally at home.
a) Ice cubes relieve swelling
Chew some ice cubes or place them at the back of your throat to help soothe the enlarged uvula. This works like a cold compress and can help relieve it fast.
b) Turmeric and ginger for anti-inflammation

Since the back of the throat swells because of inflammation and irritation, you can use herbs that have anti-inflammation properties. Turmeric, as well as ginger, are some of the home remedies for a sore uvula. Here’s how to use turmeric remedy.
- In a glass of water, mix half a tablespoon of turmeric powder.
- Add a few ice cubes to make the solution cold.
- Drink the mixture and try to let it stay in the mouth for about 15 seconds.
This will treat uvulitis faster.
c) Drink lots of water to hydrate
If you have been drinking a lot of alcohol lately, uvulitis and swollen tonsils could be caused by dehydration. The simple home remedy that will get rid of the irritation in your throat is drinking lots of water to relieve the dryness in your throat. Drink at least 8 glasses of water every day.
d) Honey remedy for swollen uvula
Honey is also an excellent home remedy to heal a sore uvula. The reason behind this is that honey is both an antibacterial and anti-fungal kitchen remedy. Here’s how to use it.
- Get pure honey for this purpose.
- Lick a teaspoon of pure honey twice a day.
- You can also swash it around your mouth to get rid of uvulitis.
If you are mixing the honey in another liquid, you can gargle with it to relieve the irritation.
e) Gargling with salt water
Saltwater can help relieve inflammation. It is used for many purposes, including unpopping congested ears and opening up a stuffy nose. You can use warm salt water rinses to reduce the swelling in your throat. Here’s how to reduce a swollen uvula by gargling saltwater.
- Half fill a glass with warm water
- Add a tablespoon of salt and mix to dissolve
- Put the water in your mouth; be careful not to put too much to choke yourself.
- Tilt your head back as you face slightly upwards.
- Now make a continuous ‘G’ sound while the water is in your throat.
- Repeat twice a day to reduce a swollen and sore uvula.
Salt contains iodine. Iodine acts as an anti-inflammatory and will also help get rid of bacterial infections at the back of the throat.
Other home remedies include chewing garlic, quitting smoking, chewing on ginger, drinking herbal tea made of ginger, cloves, black pepper, and holy basil. These will help cure the inflammation on the uvula and tonsils overnight. Antiseptic mouthwashes such as Listerine can also help you heal a uvula that is swelling overnight.
When to see a doctor?
See an ENT doctor if you see any of the following symptoms associated with uvulitis.
- Red patches on the uvula, bleeding, and inflammation.
- Blood and mucus coating the back of the tongue and the uvula, epiglottis, and back of the throat.
- Severe pain when swallowing.
- Difficulty in breathing and swallowing.
- A grunting noise in the throat when breathing.
- Constant nausea.
- Pus from the uvula.
In case of an emergency, CALL 911 FOR QUICK HELP. Difficulty in breathing and choking are considered emergencies and should be attended immediately.
Sources and references
- Fauquier ENT: Uvulectomy (Uvula Excision) for Snoring: http://www.fauquierent.net/uvula.htm
- eMedicine HEALTH: strep Throat Symptoms: http://www.emedicinehealth.com/strep_throat/page2_em.htm#strep_throat_symptoms
- The Student Room: Smoking and swollen throat: http://www.thestudentroom.co.uk/showthread.php?t=1512074
- CNN: Think snoring is normal? Why sleep apnea shouldn’t be ignored: http://edition.cnn.com/2015/01/28/health/feat-snoring-normal/
- Postgraduate Medical Journal: Long uvula: an unusual cause of chronic cough: http://pmj.bmj.com/content/80/940/116.full
- MedicineNet: Snoring: http://www.medicinenet.com/snoring/page2.htm