A dry skin on scrotum or testicle sack can be caused by some STDs, eczema or dermatitis. The dry skin can spread to the shaft and entire groin area. After vasectomy, you can also get a dry flaking skin on your scrotum. Here are the causes and treatments for dry skin on balls.
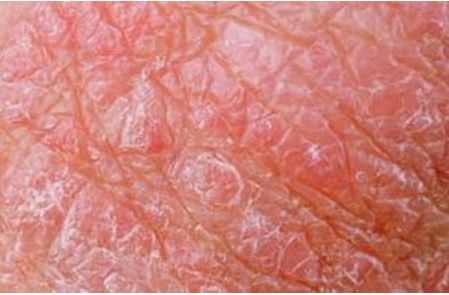
Dry, red skin on the scrotum is a fairly common problem and is not something to get worried about since everyone experiences it at some point or the other.
Since the scrotal area provides optimum conditions for bacterial and fungal growth, most problems about dry, red skin on the scrotum can be solved with anti-fungal or anti-bacterial creams and good personal hygiene.
However, other conditions that may cause these symptoms are eczema and psoriasis.
What causes dry flaky skin on scrotum?
There are many things that may cause a man to have dry flaky skin on his scrotum. For starters, this problem can occur simply because his skin is dry in general, and sometimes dry, irritated skin develops in this area because it is very sensitive.
Even something as simple as pants or underwear that chafe the groin may contribute to dry skin in the scrotum or testicles. A skin condition such as eczema may be at fault in some cases, and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and other types of infections cause dry skin on the scrotum as well.
Often, dry skin around the scrotum or balls doesn’t develop because a person has a skin condition or another type of underlying problem; it may develop just because a man is prone to this condition. In such a case, there are some easy steps he can take to deal with this issue if it affects his scrotum.
Most cases of dry, red skin on the scrotum occur during the summer months since the conditions are optimal for bacterial growth because of excessive sweating. This could worsen if you wear synthetic clothes that do not allow oxygen to reach the scrotum.
In other cases, poor hygiene may be the cause.
Dry skin on scrotum STD – herpes, HIV
The virus HIV weakens your immune system by destroying important CD4 cells, sometimes referred to as helper T cells, that fight infection. HIV takes over the T cells by making thousands of copies of the virus that damage your body’s T cells, weakening the immune system.
STD symptoms of HIV can include lack of energy, weight loss, frequent fevers, sweats, persistent or frequent yeast infections, persistent dry or flaky skin especially around the scrotum/ balls in men, short-term memory loss, and mouth/genital or anal sores.
Scrotal Eczema and Dermatitis
Scrotal dermatitis is characterized by severe itching, erythema, scaling and lichenification of the scrotal skin. Several factors are responsible for the condition, the most important being psychological stress and contact dermatitis either allergic or irritant.
The condition has been easily overlooked as fungal infection of the scrotal area. Due to wide spread use of antiseptics and over the counter topical agents, this condition is very common nowadays.
Scrotal dermatitis may be considered as an end result of various insults to the skin either patient induced or as a result of the pathological process. The symptoms vary depending on the etiological factors.
The main pathology, like elsewhere is the persistent inflammation of the scrotal skin leading to the release of the various inflammatory mediators and this evokes continuous scratching of the scrotal skin leading to further aggravation of the inflammation and thus begins a vicious cycle which finally culminates in a lichenified scrotum.
Dry Itchy Skin after Shaving Groin Area
You may find that you experience dry itchy skin after shaving the groin area. This can be brought about by a number of factors. These include:
- Using a blunt razor to shave-this only serves to cause irritation around your scrotum. This is because the blunt razor does not cut much of the groin area hair but attaches itself to the hair you intend to cut without necessarily cutting it.
This causes a tagging movement which later causes your groin area to be dry an itchy.
- Not lathering the area you intend to shave. Lathering agents are ideal as they help soften the area you want to shave thus reducing damage to the skin.
- Not moisturizing after shaving. Moisturizers serve to soothe the area you have shaved thus reducing skin irritation.
Dry Skin on Balls after Vasectomy
Most men report feeling sore, or uncomfortable for a few days. Most men also report bruising (sometimes spectacular!), and swelling. The bruising and swelling doesn’t always happen immediately – it often happens after a few days but in most cases has mostly disappeared after two weeks.
Allergic reaction to anaesthesia– A few men will develop itching & hives due to an allergic reaction to anaesthesia.
Allergy to chromic sutures:
This is quite rare, but worth mentioning. The material used to sew up the incision after many surgical procedures (including vasectomy) is known as “Surgical Gut”, and is derived from the small intestine of healthy sheep.
It’s fine-grained, has great tensile strength and elasticity. By tanning it in varying amounts of salt of chromic acid, the delay time for tissue absorption is set. Some people are allergic to Chromic acid.
Reactions to this material are difficult to diagnose post-operatively. They may be interpreted as non-specific complications of surgery. Some men who have undergone a vasectomy report still experiencing very aggravating stinging/burning/itching pain at the incision sites 10 days after their vasectomy, and their doctors diagnosed this as an allergy to the sutures.
Related symptoms for dry shaft, scrotum and groin area
Patches under or below scrotum
Strictly speaking jock itch is not a scrotal lesion, at least initially. It usually starts in the groin area that may later involve scrotum. It tends to produce itch and redness in the affected area.
It’s due to a superficial fungal infection called dermatophytes, which is caused by Tinea Cruris. It is also known as ringworm, a misnomer since the causative agent is not actually a worm, but a fungus.
It is associated with heavy sweating and rubbing of inner thighs with scrotum in the groin area. That is why it’s commoner during conditions of excessive heat and moisture.
While it is possible for the “Jock Itch” fungus to spread from the inner thigh and groin areas to the scrotum, it is almost impossible for the fungus to start in the scrotum.
So, if someone really did have jock itch fungus all over the upper thight and groin area, then it would be possible for the scrotum to eventually become affected, even though the skin on the scrotum is generally resistant to Jock Itch fungus.
However, if only the scrotum is irritated, then there is a very high probability that you have scrotal skin irritation, not a fungal infection. Using any medicated treatments on the scrotum when it is irritated will only make it worse.
Cracked and flaky skin on balls or scrotum
This is also caused by the jock itch. The rash is raised, pinkish red, flaky, cracking, peeling and very itchy. It consists of circumscribed lesions consisting of small, multiple pinpoint-like pinkish bumps. Lesion’s central area may consist of dry scales with distinct edges.
Jock itch is associated with:
- Excess moisture and sweating
- Tight underwear
- Rubbing and friction of skin
- Fungal infection
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Long term use of corticosteroids
- Improper hygiene of groin area
Painful itchy skin and testicles
This may be caused by a number of skin conditions. These include:
Candidiasis may be caused by sexual contact with an infected person (“ping-pong” infection) or from using antibiotics that disturb the gut bacteria flora. The yeast infection typically causes irritation, burning, itching and pain in the groin area.
Tinea cruris (dermatophyte infection – a kind of fungal infection also called jock itch): This is an itchy, irritable rash in the groin area that mostly affects men. It is typically associated with sweating and tight clothing.
Eczema: This is a chronic skin condition marked by itching, inflammation, redness, and swelling of the skin. While there’s no cure for eczema, it can be treated to prevent flare-ups.
Extramammary Paget’s disease of the scrotal skin is a skin cancer that may look similar to eczema. If an eczematous rash does not respond to treatment, this more serious condition is suspected. This rash sometimes involves the groin and the anal skin.
See also:
Itchy Penis Head, Shaft, Tip with Rash, Red Bumps, and Dry Skin, Treatment
Testicular Cyst Causes, Pictures, Symptoms and Treatment for a Cyst on Testicle
Discolored skin in scrotum area and thighs
If the discoloration is without itching then this is likely to be acanthosis nigricans or pseudoacanthosis nigricans if you are obese. If they are itchy it is likely to be neurodermatitis.
Acanthosis nigricans is a skin condition characterized by areas of dark, velvety discoloration in body folds and creases. The affected skin can become thickened. Most often, acanthosis nigricans affects your armpits, groin area, inner thighs and neck.
The skin changes of acanthosis nigricans typically occur in people who are obese or have diabetes. Children who develop the condition are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Rarely, acanthosis nigricans can be a warning sign of a cancerous tumor in an internal organ, such as the stomach or liver.
Redness on scrotum from irritation
Psoriasis: This chronic skin disorder is marked by raised areas of red, thickened skin with silvery scales on the knees, elbows, lower back and scalp.
When psoriasis affects the groin, it looks different from psoriasis elsewhere because the moisture in the groin area makes the psoriasis appear in red patches instead of thickened, scaly skin.
Additionally, people who have diabetes also experience redness and irritation around their groin area. Diabetes causes the rise of skin conditions which are often related to it. One of these are fungal infections.
Warm, moist folds of the skin are the perfect breeding ground for these infections.
Three common fungal infections are:
- Jock itch (red, itchy area on the genitals and the inside of the thighs)
- Athlete’s foot (affects the skin between the toes)
- Ringworm (ring-shaped, scaly patches that can itch or blister and appear on the feet, groin, chest, stomach, scalp, or nails).
How to Get Rid of Dry Skin on Scrotum and Balls
Drink More Water
Drinking too little water, especially after exercise can cause dehydration. Being adequately hydrated with fresh, clean water helps protect against excessive skin dryness.
Creams
Application of topical treatments for dry, red skin on the scrotum. These anti-fungal or anti-bacterial creams can be purchased over the counter however, if your condition does not improve with these creams, you must consult a doctor.
One of the best creams we can recommend is Antifungal Balm from FineVine
Also, in conditions such as eczema, such creams may not treat the problem.
Avoid Hot Baths and Showers
Try to avoid taking very hot showers or baths, which can make drying of your skin worse. Hot water and steam can take away the natural moisture in your skin.
Use a Moisturizer
Apply a skin moisturizer that is fragrance-free and dye-free on the affected areas to improve skin hydration. You can also use topical treatments consisting of anti-bacterial or anti-fungal creams, which can be bought over the counter to relieve dry, itchy skin. Our favourite is the one from CeraVe (Check price on Amazon)
Wash and Dry Groin Area Daily
It is important to keep your groin clean and healthy because fungi grow in warm and moist areas like the groin. Keeping it dry will prevent the fungi from growing and causing skin infection.
Change Your Underwear Daily
Wearing unclean underwear can encourage the growth of fungi in the skin flakes, which can lead to infection. It is also best to change your underwear after sweaty workouts and after each bath. Wear 100% cotton underwear to keep sweat away and prevent skin irritation.
Use Your Own Towel
Use a fresh towel after your workouts and avoid sharing them in the gym. Wear slippers in public bathrooms where bacteria and fungi are present. Fungi on the floor can cause infection in feet that can spread to your groin.
Use Fragrance-Free Soap
Your itchy skin may simply be a reaction to harsh chemicals found in soaps. Avoid bubble baths and medicated soaps. Switch to a mild cleanser and gently wash your skin twice daily. Use a special laundry detergent for sensitive skin and avoid using fabric softener or bleach.
Recommended article: 10 Best Antibacterial Body Wash Products Reviewed
Keep Your Private Parts Dry
Thoroughly dry the genital area with a clean towel after you exercise and shower. You can also use an unscented powder to avoid moisture in this area.
Resources:
- BuddyMD: Causes and Management of Scrotum Skin Rash.
- Health Xchange: Top Tips for Testicular Itching.



This article helped me a lot. I was scared I had an STD, after googling it and reading this article I discovered It was just from a new brand of boxers I recently started wearing.
This helped me SO MUCH I was filled with fear after my foreskin inflated, I started drinking more water and it went away!! Then the scabs on my testicles started growing, I peeled them off now they’re always itchy and after I read I immediately did everything they said. THANK YOU!! ??❤️❤️
John Christian Perez, how did it go since?
After hitting age 50+, the underside of my scrotum started getting itchy. Scratching felt good, but only made it worse. I tried all of the anti-fungal creams and they didn’t solve the problem (some made it worse). I got a prescription cream from my doctor that helped, but after travelling without the prescription and looking for a temporary solution, I came to realize that I only needed a moisturizer once a day to prevent the skin from becoming dry and irritated. I initially used coconut oil because it had anti-fungal properties, but later discovered that other moisturizers like baby oil (cheaper) worked equally well. It only takes a little and no more itching!