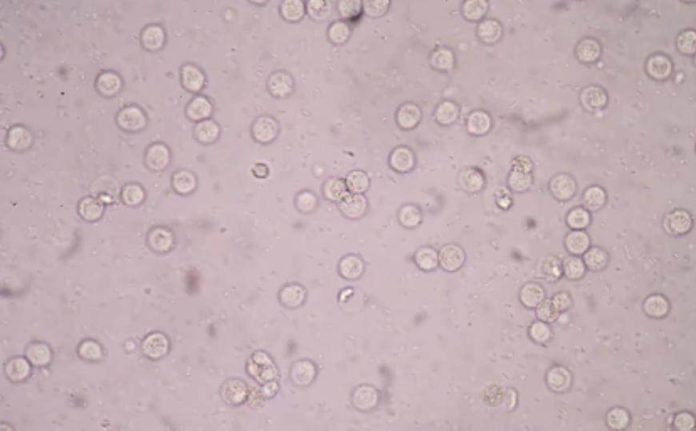
What does it mean to have white blood cells in your urine?
Normally there are no blood cells that is in the urine because the kidney does not always allow the blood cells to pass through into the urine and the blood also has no contact with the urine in any given way.
If in any case that there is an infection of the kidneys or even the bladder or if there is an inflammation because of the presence of the stones, immune disorders or growths that are found anywhere along the genitourinary system, then the blood is able to get into the urine.
White blood cells in urine causes
Conditions that are affecting the urinary tract is able to make daily tasks very much uncomfortable. Urine is usually sterile and does not have any blood cells.
SEE ALSO:
The availability of the white blood cells in a urine sample shows an abnormal condition that is within the urinary tract or even the kidney. The kidney, bladder or other parts of the urinary tract can be inflamed or even infected.
Cancer
The initial indications and also the symptoms of the bladder cancer are normally mistaken for the symptoms of a urinary tract infection.
Symptoms normally come and disappear, and are not very much severe. The most common symptoms that are felt include the below:
1. Hematuria (blood in urine)
The most common indication of bladder cancer is normally the blood that is found in the urine. Hematuria brought about by cancer is normally visible (turns the urine pink or even red), and does not lead to pain. But, people who have microscopic hematuria (the situation when blood is much visible using a microscope but do not change the urine color) also can rarely have the bladder cancer.
However, this condition happens commonly in the individuals who do not have any signs of bladder cancer. In one research, only about 15 percent of people who have visible hematuria and 5 percent of the people who have microscopic hematuria had the bladder cancer
Anyone who is over the age of 40 years old who has the visible blood in their urine should have a full evaluation of the following parts:
- kidneys
- bladder
- urethra
More especially men who are smokers.
2. Pain
Pain might also be an indication of bladder cancer. Pain is able to develop in the flank (sides of the mid-back part), which is above the pubic bone, or even in the perineum (which is the space that is between the vagina or the penis, and the rectum). Pain in the region is able to develop when there is full or even partial blockage of the ureter on that side, with the pain being because of the back pressure of the urine.
Pain can also happen during urinating a situation that is known as dysuria.
UTI
A urinary tract infection is a very common cause of white blood cells in urine. Bacteria usually enter the urethra and then travel up to the bladder, leading to the cystitis, which is an infection of the bladder. Women have a bit shorter urethras compared to the men, thus making the women to be more prone to the infections.
In men, infection can begin in the prostate and then move up into the bladder, leading to the cystitis. Symptoms of UTI are the urinary frequency, urgency to urinate after every few minutes and also the pain that is just above the pubic bone. Antibiotics are usually used in treatment of the UTIs.
STDs and white blood cells in urine
People suffering from STDs such as the gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc., can sometimes get urinary tract infections also, which further leads to high number of white blood cells in urine. It can also lead to swelling of the genitals. Pregnancy can as well result in white blood cells contamination, which increases the count of leukocytes.
1. Interstitial Cystitis
Unlike the UTI, interstitial cystitis is not brought about by infection. White blood cells that are in the urine are brought about by inflammation of the bladder wall. This condition is much common in women than in men, and leads to urinary urgency, frequency as well as the pelvic pain.
This condition is usually treated by use of the oral medications so as to
- protect the mucous lining of the bladder
- reduce inflammation
- adjust hormone levels
- reduce the pain
If conservative treatment is not applied successfully, surgery may be needed.
2. Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis may lead to white blood cells in urine. Symptoms of the pyelonephritis include;
- severe pain
- malaise
- vomiting
This condition is brought about by bacterial or viral infections, and is usually treated by use of antibiotics. Pyelonephritis also affects people of all ages, but is very much common amongst the women.
The infection begins from urinary tract, and spreads towards the kidneys. As indicated, kidneys are very much responsible for filtering of the blood, and never allows the white blood cells to enter the urine.
Thus, if the kidneys are not functioning as expected and are much affected by any kind of infection, this will provide a way for the white blood cells to pass through the kidneys into the urine. Pyelonephritis is very much common amongst the women than men.
3. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones prevents the passage of urine that is in the urethra. Therefore, urine stagnates, therefore increasing the risk of the bacterial infection. Irritation of urethra from the stones can also lead to the white blood cells in urine. Kidney stones lead to severe pain that can come in waves, making it very much difficult for you to stay in a single position.
If the stone is blocking the passage of urethra, it can be very much difficult to urinate or you can urinate only in very small amounts at one given time. Bladder spasms and also the pain during urination may also happen. People who have had a kidney stone are likely to experience more. If the stones are very large to pass through the urinary tract, they can be broken up using the ultrasound or even surgically removed.
White blood cells in urine but no infection
Interstitial cystitis happens because of the inflammation of bladder but it is not brought about by an infection. The white blood cells is able to appear in the urine when the bladder is much inflamed because of other causes other than an infection.
Interstitial cystitis happens more amongst the women than men. It leads to an individual to have a pelvic pain and urinary urgency.
Most of the women can be familiar with the problems of frequent urinary tract infections, or even apparent symptoms for which no given bacterial infection is able to be found.
Causes;
Urethral Syndrome
While the symptoms of frequency or urgency or the pain are available in almost all true infections, about 50% of patients who experience these symptoms do not have enough amount of bacteria in their urine. But, many of the people without the bacteria can have the white blood cells (which is an indication of infection or even an inflammation) in the urine.
This likely shows the presence of other infections that might not be bacterial. The presence of the white blood cells, no bacteria, and UTI symptoms is a common description of what is known as the “urethral syndrome.”
Most of the organisms are said to be the causes of urethral syndrome are also the causes of vaginal infections. Included in this particular category are;
- Chlamydia
- urealyticum
- gonorrhea
- trichomoniasis
In a study of about 70 women who had urethral syndrome, evidence for the chlamydia was found in about 42% of the group. The organism urealyticum was also identified in about 189 women who had urethral syndrome. Gonorrhea is able to infect the urethra in both the men and women. Trichomoniads can get through the female urethra from the vaginal secretions (or even the infected male ejaculate).
Less commonly, a genital herpes lesion that is within the urethra is able to prompt the urinary symptoms. Even the yeast infection of the vagina, while it does not infect the urethra, can be largely associated with the pain as the urine stream do touch the irritated skin of the vulva. Fortunately, the yeast may be seen on a microscope slide of the vaginal secretions.
This is one reason as to why continued urethral infection symptoms require to be seen by the doctor rather than use of telephoned prescriptions.
Once the organism is positively identified as appropriate, then the medications may be given. In a treatment study for the chlamydia that is affecting the urethra, researchers also determined that women would need a longer antibiotic dosing period than the ones used for vaginal or even the cervical chlamydia .
If urethral symptoms had been available for a period of about three weeks or even longer, then a better cure rates would have been achieved with six days dose of drugs such as the azithromycin or even fourteen days of doxycycline. For those who have ureaplasma, the best dose was also an extended period of azithromycin for about 7 days.
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
Overactive Bladder can be able to be distinguished from a UTI, or even a urethral syndrome, by the absence of any type of infection. Moreover, it does not lead to pain with voiding. Most of the women have smaller episodes of the incontinence where very large amounts of the urine are suddenly released.
Most of the doctors are much adept at diagnosing of the condition; it can be able to be confirmed by the urodynamic studies. The condition is also said to be brought about by the inappropriate firing of the nerves that are in the bladder wall.
Anatomic Abnormalities
Less much commonly, pain together with urgency as well as frequency might indicate an anatomic problem. From a list of conditions, a cyst of the Skene’s gland, and narrowing of the urethra are some of the conditions to be ruled out. A urethral diverticulum is a very small “pouch” that is in the urethral canal where the urine is able to collect.
Interstitial Cystitis
This condition is characterized by the urinary frequency, and also the lower abdominal pain where no identifiable pathology is able to be found. It can also be misdiagnosed as the chronic UTI, or even chronic pelvic pain. Unlike a UTI, pain mostly tends to improve with some urination.
Unlike the chronic pelvic pain, it is found that pain above the pubic bone as well as the pain in the urethra were common than the genital pain among 220 women who had the conditioned.
The causes of the condition are much debated. Each cause has a very different treatment modality.
- A defect that is in the layer of mucus that normally protects the bladder wall from any direct contact with the urine.This is a defect that is in the mucus layer has been brought about from a severe UTI, or even some other trauma. Thus, the irritants that are in the urine usually create a lot of inflammation, and also much increased pain signals to the brain.
Treatments are avoidance of caffeine, artificial sweeteners, and spicy and also the acidic foods. There are two approved prescriptive drugs. One is a pill that is taken for three times per day. The other is the one that is instilled directly in the bladder by the urologist
- A neurological disorder that is in pain processing pathways of the CNS. The limbic system in the brain has a lot of sensitivity to the pain signals that emanates from pelvic organs, which then triggers the muscle contractions that are in the involved area.
Treatments are not submitted to for approval but normally used are: amitriptyline or local anesthetics that are instilled in the bladder by your urologist.
- The presence of the tissue is transforming of one cell type into a mature cell type that is in the bladder neck region.Women who are not receiving any relief from the medications are supposed to be treated using a laser to get rid of the metaplasia.
Overall, the condition is perceived to be a very complex condition that has no clearly identified cause. As such, most of the treatment options might be combined. The addition of the biofeedback, education, and also the support can enhance the response that is directed to the treatment
Bottom line
If you are experiencing symptoms of a urethral infection, then you should be checked out using at least a urine dipstick. Treat perfectly using the antibiotics if they are indicated and expect that the symptoms might take about four days to start improving. If the symptoms return, then go back for a follow up.
If you are a woman that has persisting urinary symptoms, and also the cultures negative for the bacteria, one of the vital things that you can do is to understand and know about some of the causes of such symptoms. A gynecologist can be relieved if you raise the issue that it might not be the bacteria in the urine that is bringing about the symptoms.
White blood cells in urine during pregnancy
Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection is the common cause of the availability of the white blood cells in the urine during the pregnancy. The reason that is behind this is that most of the pregnant women are much more susceptible to the urinary tract infections than the women who are not pregnant.
There is a much clear reason for this. Throughout the pregnancy the baby is growing and the pressure that is exerted on the bladder is thus increasing. Therefore, even though the volume of bladder is increased in size, the tone of the bladder is also suppressed.
Kidney Infection
Urinary tract infections are supposed to be treated the perfectly. If they are not in any way treated, the kidneys also might thus be infected. Such kind of infection of the kidneys is known as the pyelonephritis and even the infection can lead to the white blood cells in urine. When the kidneys are infected, you will begin to vomit. You can then start to feel very nauseous and can even experience very high fever.
Additionally, you can start to have a lot of pain in the sides and even the lower back. The infection is supposed to be treated right away so as to avoid any other complications like the premature membrane ruptures and also the premature labor. The infection is able to be treated by use of antibiotics. This infection is the reason as to why most of the pregnant women are usually hospitalized.
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is normally the condition where several bacteria begin to multiply in the urinary tract and indicate no symptoms at all. This is able to be detected via a urine test since the urine will show the presence of the leukocytes if you are suffering from the condition. You should have it treated right away by use of antibiotics since if you leave it to be untreated, it can cause several complications.
Treatment for white blood cells in urine sample
These are the common courses of the treatment that is undertaken according to the causes of white blood cells in urine:
Kidney stones
- Treatment depends on how large the particular stone is
- Anti-inflammatory medication is normally administered to assist the patient to deal with the symptoms
- Drinking of large quantities of water assists much for a person to eliminate the stone
- Lithotripsy – sound waves are applied for the stone to be broken into smaller pieces, therefore allowing an easier removal process
- Surgical removal – this is recommended only in very serious cases
- Antibiotics – get rid of the infectious organisms
Urinary tract infection
- Broad spectrum antibiotics are used
- Drinking large amount of water assists to get rid of the infectious organisms faster
- Intravenous antibiotics are normally recommended in the case of very serious infection, with the life-threatening symptoms
Cystitis
- Anti-inflammatory medication –the ones that provide pain relief
- Antibiotics – mostly in case of any associated bacterial infection
- Medication that are used to bring spasm relief
Interstitial cystitis
- Anti-inflammatory medication that are used for the symptoms
- Physiotherapy is used to strengthen muscles
- Transcutaneous nerve stimulation
- Medication administered directly into the bladder
Cancer
- Chemotherapy is used
- Radiotherapy is sometimes aplied
- Surgery in very rare cases
Pyelonephritis
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics to get rid of the infectious organisms
- Hospitalization is needed when life-threatening symptoms are brought about by the infection
Urinary tract obstruction
- Temporary solution – urinary stent
- Surgery for getting rid of the obstruction
- Laparoscopic surgery – minimally invasive procedure, which has good results
Further references;
- What are the Causes of Leukocytes in the Urine in Pregnancy: http://www.conceiveeasy.com/get-pregnant/what-are-the-causes-of-leukocytes-in-the-urine-in-pregnancy/
- White Blood Cells in Urine: http://mddk.com/white-blood-cells-in-urine.html
- Causes of White Blood Cells in Urine: http://www.livestrong.com/article/81433-causes-white-blood-cells-urine/
- White blood cells in urine: http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/ask-the-expert/liver-kidney-and-urinary-system/a2942/white-blood-cells-in-urine/
- BLADDER CANCER SYMPTOMS: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/bladder-cancer-diagnosis-and-staging-beyond-the-basics
- White Blood Cells in Urine: http://www.buzzle.com/articles/white-blood-cells-in-urine.html
- What do White Blood Cells in Urine mean: http://healthylifemed.com/what-do-white-blood-cells-in-urine-mean/