What causes the swollen gland under the tongue? A lymph node or a lymph gland is a small organ in the body that produces white blood cells that help the body fight infections. These glands are distributed throughout your body. They can become swollen or enlarged as a result of fight viral and bacterial infections.
Under the tongue, these glands are likely to swell as a result of a common cold, strep throat, infectious wound, or due to canker sores. Enlarge lymph nodes are harmless and will often regain their original size without the need for treatment.
Causes of the swollen gland under tongue
Many causes can cause swollen lymph nodes under the tongue. For most people, a swollen gland is likely to indicate an underlying infection that can either be viral or bacterial. As mentioned, enlarge glands are harmless and will often regain their size after the infection clears.
1. Cancer
Though very rare, the glands under the tongue may swell due to salivary gland cancer. According to the Mayo Clinic, it is not known what the exact cause of salivary gland cancer is.
It is, however, believed to occur when some cells in a salivary gland develop a mutation in their DNA. The mutation is what enables them to grow and divide rapidly.
The risk of salivary gland cancer increases with old age, exposure to radiation, and harmful substances. Apart from the swollen glands under the tongue, salivary gland cancer can be shown by the following symptoms:
- A hard lump near the jaws
- Numbness in part of the face
- Pain around the salivary gland
- An irregular shaped lump occurring deep in tissue
2. Blocked salivary glands
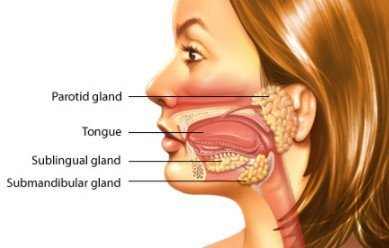
Salivary glands are responsible for producing saliva that keeps lubricating your mouth. This helps with swallowing, protecting your teeth against bacteria, and aid in digestion. There are three major salivary glands:
- Sublingual glands under the tongue,
- Parotid gland on the inside of cheek and
- Submandibular glands at the floor of the mouth
A problem such as a blocked salivary gland can be shown by painful swelling of the glands, dry mouth, fever, and foul-tasting drainage into the mouth.
A blocked salivary gland is often a result of a bacterial infection, which results from reduced saliva production. Your salivary gland may also swell or become inflamed as a result of Mumps, herpes, poor oral hygiene dehydration, among other causes.
3. Parotid gland stones
Parotid glands are two large salivary glands located one on each side of the cheek over the jaw. Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both of these glands can cause the swelling of the glands under tongue. Parotitis can be caused by many conditions.
- Minor bacterial infections cause acute bacterial parotitis. This causes pain, redness, swelling, and tenderness over the glands on the side of the cheek.
- Chronic recurrent parotitis is characterized by repeated episodes of swelling of the parotid glands most commonly after eating. It is caused by decreased saliva flow. It can also be caused by the blocking of the duct by stone or narrowing of the duct structure.
- Parotid gland stones can also be caused by a viral infection. The most common viral infection that might lead to the inflammation of the parotid glands is mumps. This condition is common in kids between 4 and 10. It is characterized by painful swelling of both the parotid glands.
4. Tongue sores
Swollen glands under the tongue can also be caused by different conditions causing tongue sore. This will include cold sore, canker sores, injuries, and trauma. Your lymph glands will swell as they try to fight and protect your body from infection and foreign bodies common to your body through the tongue sores.
5. Sore throat
A sore throat is a viral infection marked with pain and irritation of the throat. The most common cause of a sore throat is a cold or flu virus. This infection is not serious and will, in most cases, clear on its own.
Strep throat, a bacterial infection, is a less common type of a sore throat. A minor case of a sore throat can be treated with antibiotics; for serious cases, complex treatment may be required to treat the infection to relieve the swollen glands under tongue.
6. Yeast infection
Your tongue and glands under the tongue are also likely to swell as a result of a yeast or fungal infection inside your mouth. Oral fungal infections are common in people who regularly take antibiotics and those with poor oral hygiene.
Yeast infection causing swollen lymph nodes under tongue can be treated with both oral and antifungal mouthwash. Proper oral hygiene can help prevent such infections.
7. Allergies
Allergic reaction to food or medicine can also be the underlying cause of a swollen gland under tongue. Some people may become allergic to blood pressure medicine or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and aspirin.
Enlarge glands caused by an allergic reaction will tend to be sudden. An allergic reaction can be life-threatening, and as such urgent medical attention is required. If the reaction was caused by a new drug you are taking, discontinue the use and consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Apart from the swollen glands, you are likely to notice an itchy rash, hives, rapid breath, and shortens in breathe among
8. Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is a common bacterial infection that develops in people with strep throat. It is more common in children below 15 years and is almost always accompanied by a sore throat and a high fever.
When left untreated, this condition can cause serious complications affecting the heart, kidney, and other organs.
The condition is treated with antibiotics. Scarlet fever can be shown by symptoms such as swollen neck glands, vomiting, and red blotches.
9. Glossitis
Glossitis is the inflammation of the tongue. This condition causes the tongue to swell, change color, and develop a smooth appearance on the surface. In cases of severe inflammation, redness and swelling can cause pain and make it hard to talk or eat.
Glossitis can either be acute, chronic, idiopathic, or atrophic, where a large number of papillae are lost, resulting in a change in the color and texture of the tongue.
10. Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid can also cause your tongue to swell. This intern may lead to the swelling of your lymph node under the tongue. This condition can be shown by:
- Dry skin
- Puffy face
- Painful and stiff joints
- Constipation among others
11. Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a rare but very serious condition caused by deposits of an abnormal protein (amyloid) in tissues and organs throughout the body. This protein can affect any organ in the body; the sign and symptom will depend on the affected organ.
See also:
- Blood Blister Under Tongue, on Tip, Side, Back of Tongue, Remedies, Treatment
- Swollen Uvula Due to Snoring, Drinking, STD – How Long Will It Last?
Swollen gland under tongue one side
Lymph nodes occur throughout the body. When occurring close to one another, lymph nodes tend to form into groups or chains. This kind of formation is common on the sides of the neck, the armpits, and the groin.
Lymph nodes under the tongue, just like those occurring in other parts of the body, are often small, pea-sized. They can be felt as small lumps under the skin. Lymph nodes on either side of the tongue can be felt in the neck.
Swollen glands under the tongue on one side are easily noticeable due to the increase in size. When the swelling is only on the right or left side of the tongue, then it means that the side of the tongue is closer to the infection than the other part of the tongue. Generally, the lymph glands near an infection swell quickly and become tender as your immune system continues to fight off the infections.
With minor infections, the swollen gland under tongue either on the right or left side of the tongue will take a short time then regain their original size. For serious infections, this may take more than a week or two. For that reason, proper treatment for the underlying condition may be required.
Swollen sublingual glands
Sublingual glands are one of the three pairs of relatively large, major salivary glands. The others being parotid glands and submandibular glands. Sublingual glands have a duct that empties onto the floor of your mouth.
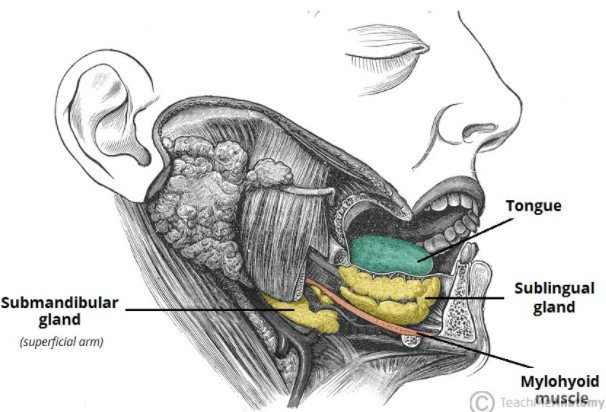
According to WebMD, the most common cause of swollen salivary gland, or salivary stones are the build-up of crystallized saliva deposits. Salivary stones can block the flow of saliva when saliva can exit through the duct. It backs up into the glands causing painful swellings. Your salivary glands are likely to get infected if the gland is not unblocked.
Pain under the tongue and swollen glands
Pain under the tongue and swollen glands are likely to be signs of a swollen parotid gland. Parotid glands are salivary glands located between the ear and the jaw. These glands are likely to swell and become painful if you develop a viral infection such as mumps or flu.
The swelling of the parotid glands will often occur on both sides of the face. In most cases, the swelling will often start approximately two days after the start of other symptoms such as fever, nausea, and headache.
Swollen gland with no pain
Swollen glands are often a sign of an underlying infection. These glands are a very important part of the immune system, which helps your body fight viral, bacterial, and other kinds of infection.
For a healthy person, these glands are pea-sized lumps of tissue containing white blood cells, when fighting an infection, the glands may swell to more than a few centimeters.
A swollen lymph node often painful and tender; depending on what the underlying cause is, you are likely to have other symptoms such as fever and night sweats. The glands may feel hard, fixed, and rapidly growing. Swollen lymph glands are harmless and will often regain their original size once the infection clears.
A swollen gland with no pain can be a sign of a cancerous growth. In such cases, an urgent medical examination may be required to diagnose the condition as soon as possible. Please consult your doctor if you notice the following symptoms:
- The node rapidly increases in size
- The swelling fails to clear within a week
- Painless swollen glands
- Unexplained weight loss
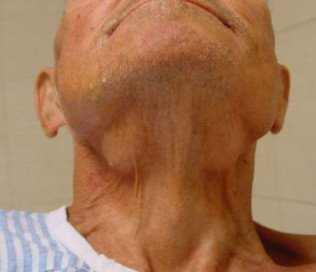
Swollen glands under tongue pictures
Here are some images of how a swollen gland under tongue looks like:
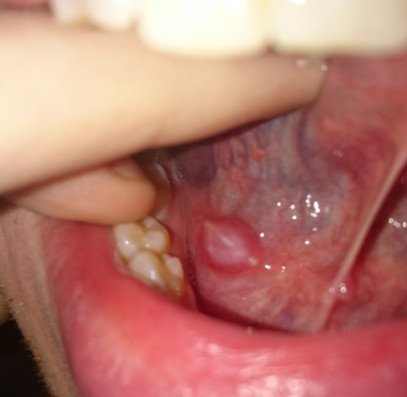
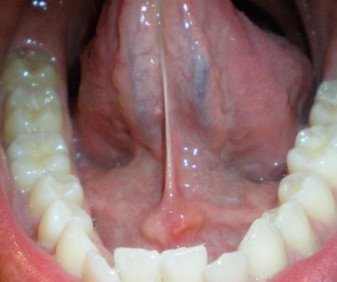
Treatment for a swollen gland under tongue
The treatment for swollen glands under the tongue will often depend on the underlying cause of the swelling. Remember, a swollen gland is not a disease, but a sign or a maker of an underlying infection that can either be minor or serious.
The glands will, in most cases, clear without treatment, but treating the underlying condition of infection is the best way to get rid of the swelling.
Treatment for swollen glands under the tongue may involve the following:
- For bacterial infection causing the swelling, antibiotics pills, or injection may be used to treat the infection the relieving the swelling of the glands.
- Antifungal and antivirals infections are used for viral infections.
- When the cause of the swelling is an allergic reaction to food or medicine, an antihistamine may be used to relieve the swelling.
- Your doctor will prescribe a specific treatment option depending on what the underlying cause of the swelling is.
Home remedies for swollen glands under the tongue
Maintain proper oral hygiene can help prevent some oral infections that might lead to the swelling of the lymph glands under tongue. This will include preventing conditions such as bacterial and viral infections.
In most cases, however, salivary gland infection that might cause swelling of the glands cannot be prevented.
Swollen or enlarge glands are rarely harmful. As said, no treatment is required in some cases to clear the swelling as the glands often regain their size after some time. There are, however, some simple self-care remedies you can use to speed up the recovery process.
Here are some effective home remedies you can use to get rid of swollen glands under the tongue:
1. Floss and brush your mouth
Floss or brush your mouth after meals to prevent bacterial infections maintaining proper oral hygiene, may help prevent and heal minor viral and bacterial infections inside your mouth.
You need to be very careful with the toothpaste you use. Use a mild toothpaste that is not allergic to your mouth. The toothbrush you use should be one with a soft bristle, when brushing, use moderate force to avoid damaging your tongue, and the inner lining of your mouth.
Our absolute favorite brushers are SmartSeries from Oral-B.
You can check it’s the current price on Amazon
2. Rinse your mouth with warm salty water
With swollen glands under the tongue, dry mouth can cause a lot of irritation and pain. Rinse your mouth repeatedly with warm water to keep your mouth moist and relieve the pain caused by the swollen glands.
Kitchen salt is a natural antibiotic, using t in your mouth may help stop and prevent bacterial infection that might be causing the swelling.
- Add a tablespoon of kitchen salt in a glass of warm water
- Gently stir to mix
- Use the resulting mixture to rinse your mouth
- Do this in intervals of two hours
3. Cut down on smoking and alcohol
If you smoke or drink alcohol, you will need to cut your consumption until the infection clears. Smoking can cause your mouth to dry out, making the swollen glands painful and irritating.
4. Drink plenty of water
Drinking plenty of water ensures your body is dehydrated. Water and sugar-free lemon drops help increase the flow of saliva. It can thus help relieve the pain and swelling of the glands under tongue.
5. A warm compress
Massaging the swollen gland with heat may help speed up the healing process. Applying a hot compress on the skin opens up the blood vessels around that area. This increases the flow of white blood cells, red blood cells, and nutrients toward that area.
This is what speeds up the healing process of the infection; thus, the lymph glands can regain their original size. For swollen glands on either side of the tongue:
- Add some hot water in a basin
- Add a tablespoon of kitchen salt or Epsom salt then stir to mix
- Dip a clean face towel, then squeeze to get rid of excess water
- Now place the towel on the affected side and hold it on for 3 minutes
- Repeat this 10 times in intervals of 2 hours
References:
- Salivary gland infections: http://www.healthline.com/health/salivary-gland-infections#overview1
- Salivary gland problems: http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/salivary-gland-problems-infections-swelling#1
- Causes and how to treat a swollen gland under tongue: http://www.tandurust.com/oral-care/swollen-gland-under-tongue.html
- Salivary gland stones: http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/salivary-gland-stones/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- Salivary gland infection, types: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001041.ht
- Causes of swollen salivary glands: http://www.healthhype.com/swollen-salivary-glands-causes-of-swelling-enlarged-gland.html


I feel like all my esophagus is burning ,I ‘m not able to see the uvula .Sometimes it hurts when I eat solid food .I feel better if I eat ice cream .I’ve been like this almost for 2 weeks .I have thyroid problems since 1983 .I’m taking LEVOTHYROXINE 0.075 MG TABS .And yeah! I’, having too many problems such as constipation also . I have a sensation of burning staring from my stomach all away to my mouth .In the morning I have a weird taste too.